The term “contract manufacturing” refers to the manufacturing services that some manufacturers perform on a contractual basis for other businesses. The companies for which they perform contract manufacturing services are called “original equipment manufacturers,” or OEMs. Contract manufacturing is also known as private label manufacturing or outsource manufacturing. Read More…
More Contract Manufacturing Companies
While “outsourcing” often implies manufacturing that takes place beyond North America’s borders, it can also denote any production that occurs outside the original equipment manufacturer (OEM).
Applications
Many businesses turn to contract manufacturing for its cost-saving benefits, enabling them to optimize their resources and afford the maintenance of costly equipment.
Contract manufacturers offer a range of services, including contract machining, contract assembly, and subcontracting, to meet diverse production needs.
They offer a diverse range of capabilities tailored to meet various industry needs. Their expertise encompasses a broad spectrum of manufacturing processes such as milling, sawing, planning, tapping, drilling, turning, boring, and grinding. In response to evolving demands, many are also adopting advanced technologies like electrical discharge machining, ultrasonic machining, and electrochemical machining.
Companies across a multitude of sectors—ranging from marine and automotive to aerospace, food and beverage, chemical, pharmaceuticals, military and defense, medicine and healthcare, and electronics—rely on these specialized contract manufacturing services to meet their production requirements.
History
Modern contract manufacturing is a relatively recent development, emerging in the mid-Space Age of the 1970s. During this period, as NASA faced declining funding for its ambitious projects, Olin King, an Alabama-based government subcontractor, began seeking new avenues for his business. He started partnering with engineering and technology firms like IBM to provide manufacturing services. This approach quickly gained traction, with companies like Solectron joining the movement. They offered to produce entire electronic products and their components. By 1981, IBM marked a milestone by unveiling their first computers manufactured by a contract producer.
During the 1980s, electronics companies increasingly turned to contract manufacturers for a variety of applications. They discovered that certain in-house manufacturing processes could lead to environmental problems. By outsourcing their engineering and assembly tasks, they effectively sidestepped these issues.
In the early ’90s, contract manufacturers began broadening their service offerings and exploring new markets, including pharmaceuticals, clothing and textiles, and toy production. This expansion was significantly driven by the advancements in CNC machining technology, which had been evolving gradually over the preceding decades. CNC machining revolutionized their capabilities, enabling faster lead times, increased production volumes, superior quality parts, tighter tolerances, and more intricate designs.
Contract manufacturing services have become exceptionally profitable in today’s world. Advances in communication and transportation have transformed contract manufacturing into a highly efficient and widely embraced production method. Although businesses have long relied on specialized tradespeople for product creation, technology now enables this process to occur on a global scale. For instance, a company in England can design parts, which are then assembled in China using materials from Brazil and sold to a firm in the United States. This trend is expected to persist, with the contract manufacturing industry growing at an annual rate of 10%. Specifically, the global contract electronics manufacturing market is expanding at approximately 15% per year, while pharmaceutical contract manufacturing is increasing at around 7.5% annually.
Service Details
This is how contract manufacturing works, from start to finish.
- Typically, a company seeking a contractor begins by advertising the project and inviting bids. This approach is particularly prevalent in government projects.
- After reviewing the bids, the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) selects several manufacturers to discuss their application with.
- Following their discussions, the OEM selects the manufacturing company of their choice and formalizes the agreement to proceed with them.
- Typically, an OEM and a contract manufacturing company enter into a contractual agreement outlining a specific project that the contract manufacturer will undertake. This agreement details the timeframe and budget agreed upon by both parties, which can span hours, days, weeks, months, or even years. While manufacturing contracts usually range from 3 to 5 years, their duration can vary significantly based on the project’s requirements.
Occasionally, they remove the timeframe entirely and substitute it with a measurable output goal. Documenting this contract is advantageous for both parties as it ensures accountability. Additionally, when an OEM collaborates with a foreign manufacturer, these written agreements help mitigate language barriers.
- After being hired, the contract manufacturer consistently produces goods or delivers services for the OEM. Typically, they affix the OEM’s company logo to the products before shipping them out.
Contract Considerations
Contract manufacturers are essential partners in crafting and planning products and services for their clients. Our role involves a deep dive into understanding each client’s specific requirements, expectations, and goals. We start with a comprehensive analysis of the client’s needs, including product specifications, quality standards, and regulatory criteria. With this foundation, our design team collaborates closely with the client to create a customized solution. This process includes conceptualizing, prototyping, and fine-tuning the product or service design until it perfectly reflects the client’s vision. We take into account several key factors—cost-efficiency, scalability, and manufacturability—during the design phase. Once the design is finalized, we meticulously plan the production process, including sourcing materials, allocating resources, and setting timelines. Our goal is to ensure that every step is executed efficiently and effectively, adhering to the agreed-upon quality standards and delivery schedules. Through our collaborative approach, we are committed to providing our customers with tailored, high-quality products and services that meet their specific needs and market demands.
Machinery Used
Contract manufacturers deploy a broad array of equipment and tools tailored to the unique demands of their clients and the specific industries they serve. Essential manufacturing and assembly tools encompass CNC machines, injection molding systems, robotic automation, and various testing apparatuses. For metalworking and fabrication, we rely on lathes, milling machines, and welding tools. In the electronics sector, our focus shifts to surface mount technology (SMT) machines, testing gear, and pick-and-place systems. We also employ packaging and labeling machinery, including blister packaging machines and labeling systems, to ensure products are presented attractively. Our quality assurance and testing equipment, such as coordinate measuring machines and environmental testing chambers, verify that products adhere to rigorous standards. For industries like pharmaceuticals and semiconductor manufacturing, we maintain controlled environments using cleanroom facilities equipped with advanced HVAC systems and air filtration units. The choice of equipment varies depending on the industry, product complexity, and client requirements, allowing us to provide high-quality, tailored manufacturing services.
Variations and Similar Services
Contract manufacturing encompasses a wide range of services, including contract machining, assembly, packaging, and various specialized areas such as nearshoring and outsourcing. We engage in industrial, military, electronic, and aerospace contract manufacturing, along with PCB assembly. Our expertise also extends to pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturing, chemical processing, and contract sewing.
Contract machining is a specialized service provided by contract manufacturing companies, where they operate their machine shops to process a range of materials. This process prepares the materials for subsequent stages of design and manufacturing.
Contract assembly services encompass the assembly of parts and products, often performed on specialized machinery such as assembly lines. These services can be carried out using manual labor or automated machinery, depending on the requirements of the project.
Contract packaging involves providing packaging services under a contractual agreement. Companies that specialize in this field, known as contract packagers or co-packers, handle both the production of items and the packaging materials. Their offerings typically include blister packaging, clamshell packaging, shrink wrap, and labeling.
Nearshoring refers to the practice of outsourcing manufacturing to a nearby country, either the same country as the hiring company or a neighboring one. This approach offers significant advantages, including reduced shipping costs and shorter project lead times.
Outsource manufacturing, while essentially synonymous with contract manufacturing, specifically denotes the contract manufacturing services that OEMs procure from international providers.
Industrial contract manufacturing specializes in producing industrial equipment and executing industrial processes. This includes a diverse range of products such as commuter rail lines, rubber goods, textiles, heavy machinery, and plastic injection-molded items. Additionally, industrial contract manufacturers may also handle the production of certain industrial electronic components.
Military contract manufacturing, also known as defense contracting, involves companies approved by the government to produce essential items for the military, including weapons, body armor, aircraft, and shelters. When not engaged in government projects, these manufacturers often diversify their income by partnering with a variety of non-governmental organizations.
Electronic contract manufacturing stands as one of the most expansive sectors within the industry. We craft a diverse array of electronic products and components, spanning everything from cell phones to semiconductors.
PCB assembly, also known as printed circuit board assembly, is a specialized area within electronic contract manufacturing. Our PCB assembly services involve the precise construction and integration of circuit boards that support a diverse array of electronic products.
Aerospace contract manufacturing involves producing components and products for a range of aerospace applications, including helicopters, jets, airplanes, and unmanned aircraft. This field demands adherence to exceptionally stringent standards, tailored to meet the specific requirements of each customer.
Pharmaceutical contract manufacturing is typically handled by specialized firms known as contract development and manufacturing companies (CDMCs) or contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs). These companies produce a variety of products for pharmaceutical clients, including liquid medicines, capsules, pills, creams, and lotions. Additionally, they manage all aspects of packaging for these products.
Medical device contract manufacturing companies specialize in producing medical devices and tools on behalf of other businesses, enabling those businesses to bring these products to market.
Chemical contract manufacturing is a specialized area within contract manufacturing that centers on producing equipment and synthesizing chemicals and materials for other companies or organizations. These chemicals and materials often serve as essential components for customers to carry out their specific applications.
Contract sewing is a specialized area within contract manufacturing that caters to OEMs by producing not just garments, but a diverse range of products including carrying cases, table umbrellas, tents, cushions, upholstery, blankets, anti-static computer cloths, and more. Our contract sewing services encompass tasks like label stitching and involve working with an extensive selection of materials, from luxurious velvet to durable vinyl.
Benefits
Both parties in a contract manufacturing arrangement enjoy numerous advantages. Opting for contract manufacturing provides significant benefits to companies looking to outsource production. Primarily, it enables businesses to concentrate on their core competencies and strategic initiatives, while leaving the manufacturing tasks to specialized experts. This approach optimizes internal resources, simplifies operations, and allows companies to invest more time and effort into areas like product development, marketing, and sales. Additionally, partnering with contract manufacturers grants access to specialized expertise and advanced technologies that might not be available internally. These manufacturers bring a wealth of industry knowledge, experience, and cutting-edge equipment, which can enhance product quality, efficiency, and innovation. Contract manufacturing provides a range of benefits, starting with its inherent flexibility and scalability, which allow companies to adjust production volumes in response to market demand. This approach reduces the need for substantial initial investments in manufacturing facilities and equipment, offering a more cost-effective solution. Additionally, it facilitates faster entry into new markets and quicker product launches by tapping into the contract manufacturer’s expertise and established infrastructure. Geographical advantages also come into play, such as the strategic location near target markets or access to cost-effective labor and raw materials, which can enhance both competitiveness and cost-efficiency. In summary, contract manufacturing delivers significant advantages, including improved focus, access to specialized knowledge and technology, adaptability, rapid market entry, and optimized costs.
As the contract manufacturer, we gain numerous advantages from engaging in contract manufacturing arrangements. Foremost, this model ensures a continuous flow of work and revenue. By working with various clients and handling production projects on a contract basis, we sustain a steady workload and make full use of our production capabilities. This approach allows us to optimize our resources, achieve economies of scale, and ultimately enhance our efficiency and profitability. Contract manufacturing also offers manufacturers the opportunity to broaden their expertise and capabilities by engaging with various industries and product categories. This diverse experience contributes to their knowledge and skill enhancement, allowing them to refine their competencies and maintain a competitive edge. Additionally, successful contract manufacturing can pave the way for long-term partnerships and repeat business. By consistently providing high-quality products and services, manufacturers can establish a reputation for reliability, making them a preferred choice for clients in search of manufacturing solutions. This approach helps secure steady, ongoing contracts and cultivates a loyal customer base. Additionally, contract manufacturing opens doors to collaboration and innovation. By partnering with diverse clients, we gain exposure to various perspectives and ideas, which stimulates creativity and drives continuous enhancement in our manufacturing processes. In essence, we enjoy the advantages of a reliable workload, skill advancement, enduring partnerships, and a dynamic environment ripe for collaborative innovation.
Things to Consider
Before finalizing an agreement with a contract manufacturer, it’s essential to evaluate several key factors. Consider whether the manufacturer utilizes advanced technology and has the capabilities to meet your standards. Assess their delivery options and timelines to ensure products will arrive as needed. Review their payment plans, reputation, and years of operation. If a manufacturer can’t meet your production and shipping deadlines, seek out another one who can.
Furthermore, any manufacturer you engage with should be open to working on a trial basis before you commit to a contract. Hesitance to offer this can signal a lack of transparency. Be cautious if they are unwilling to negotiate payment plans, discuss customizations, or provide quality assurances, as these are additional warning signs.
Most contract manufacturers strive to prove their reliability and position themselves as ideal long-term partners. They take pride in showcasing their organizational skills and their ability to meticulously track customer orders. If a potential contract manufacturer doesn’t convey these qualities, it’s wise to proceed with caution. Unreliable manufacturers can lead to significant issues, including delivering substandard goods or services. Additionally, if you’re sharing proprietary technology and specifications, a dishonest partner could embroil you in intellectual property disputes.
Global communication has streamlined the process of advertising, bidding on manufacturing contracts, and managing production orders. However, identifying a reliable pool of contract manufacturers can still be challenging. To assist you, we’ve compiled a list of contract manufacturers known for their high-quality work, which you’ll find interspersed between these paragraphs. For optimal results, we suggest reviewing their capabilities and offers, then narrowing your choices to three or four candidates. After reaching out to each to discuss your project, select the one that best meets your needs and negotiate the contract with them.

Aerospace Contract Manufacturing
Chemical Contract Manufacturing
Contract Manufacturers
Electronic Contract Manufacturing
Medical Device Contract Manufacturing
Military Contract Manufacturing
Outsource Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing











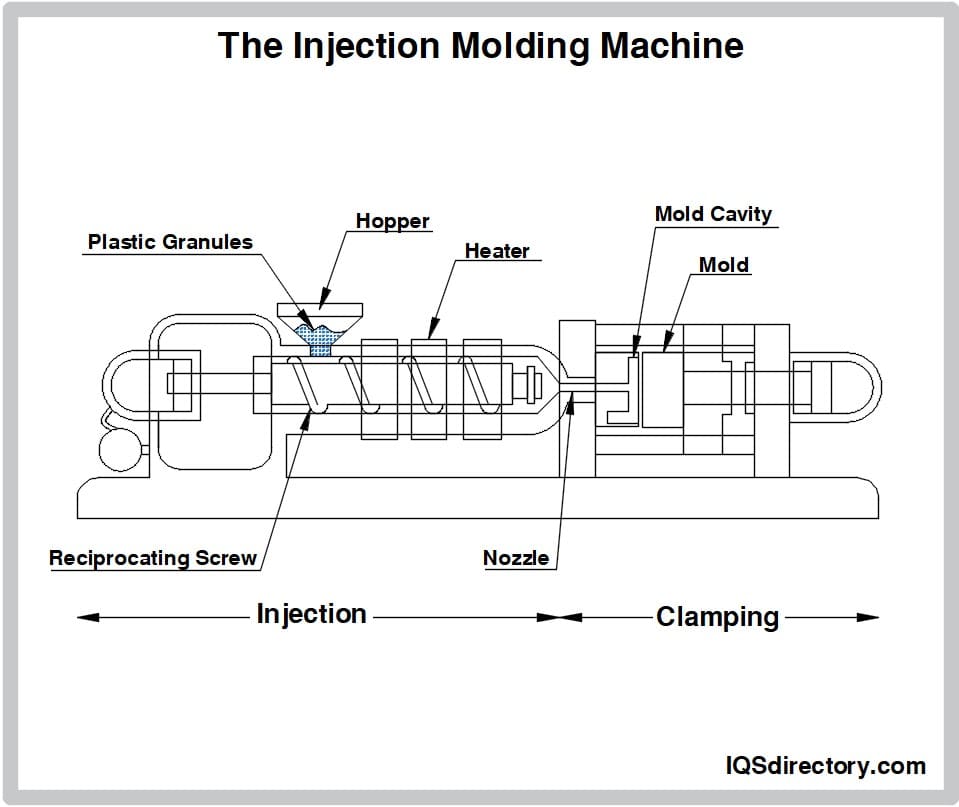
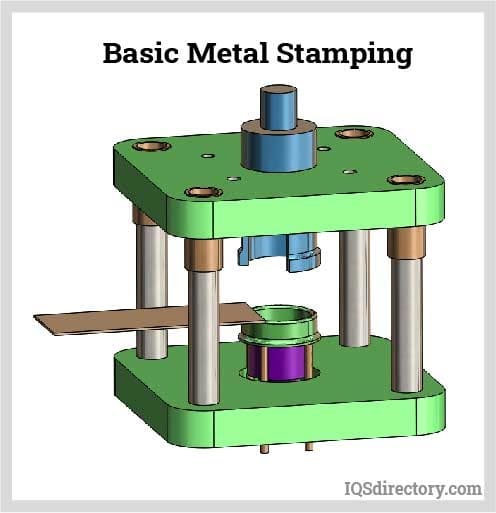
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions Broaching
Broaching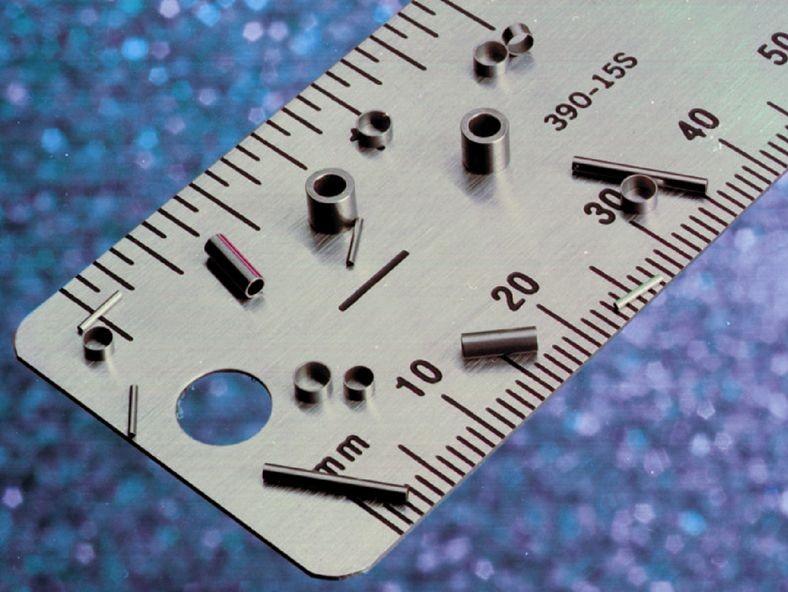 CNC Machining
CNC Machining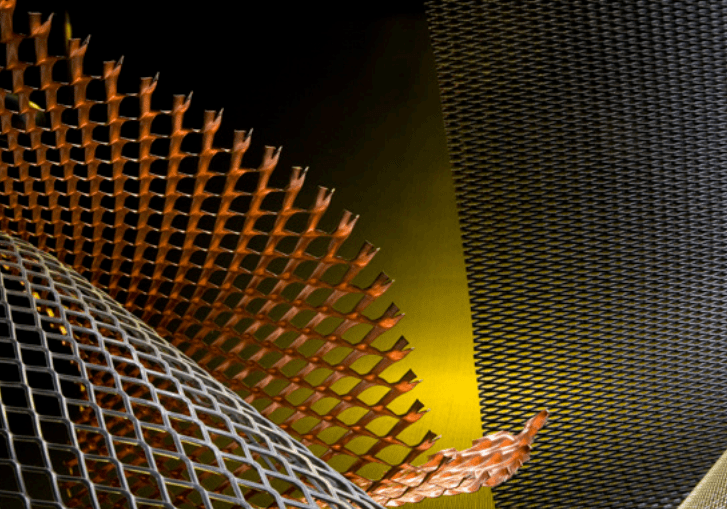 Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting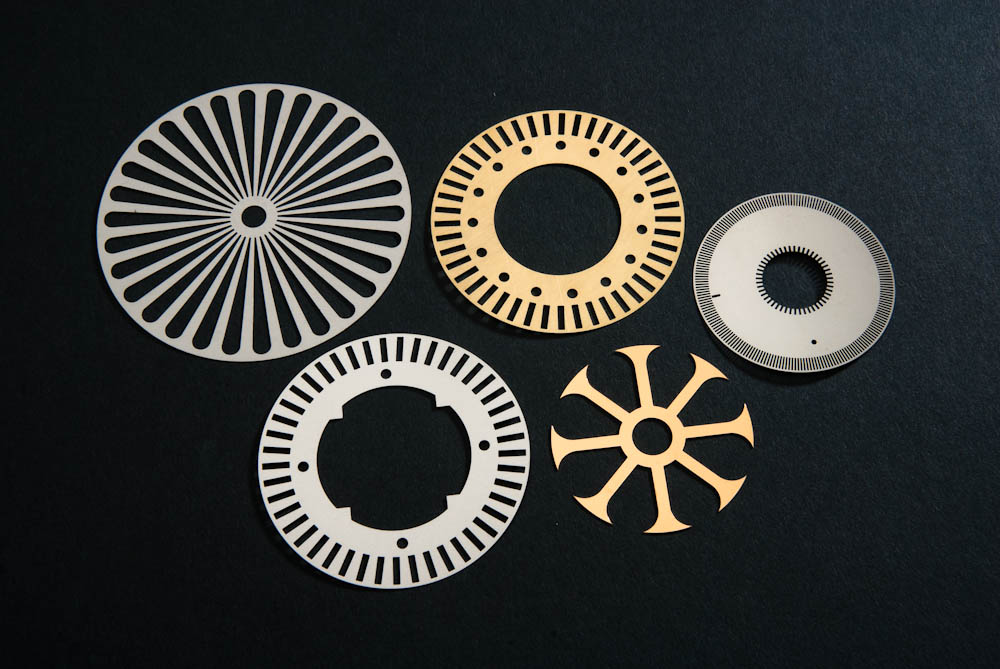 Metal Etching
Metal Etching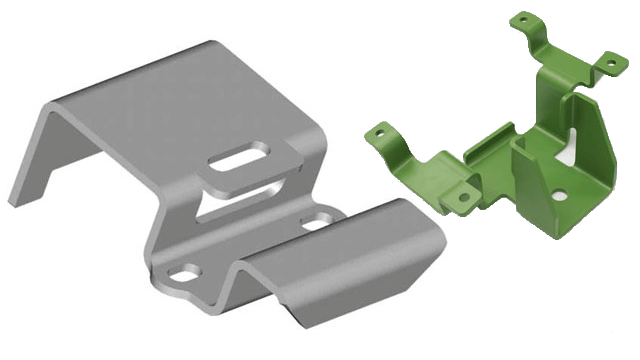 Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings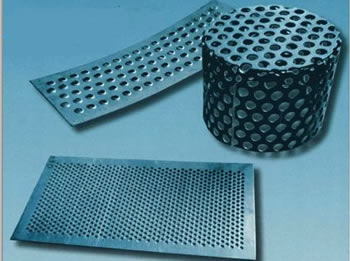 Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers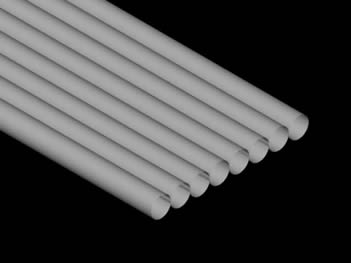 Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services